Project forking workflow (FREE)
Whenever possible, it's recommended to work in a common Git repository and use branching strategies to manage your work. However, if you do not have write access for the repository you want to contribute to, you can create a fork.
A fork is a personal copy of the repository and all its branches, which you create in a namespace of your choice. Make changes in your own fork and submit them through a merge request to the repository you don't have access to.
Create a fork
- Introduced a new form in GitLab 13.11 with a flag named
fork_project_form. Disabled by default.- Enabled on GitLab.com and self-managed in GitLab 14.8. Feature flag
fork_project_formremoved.
To fork an existing project in GitLab:
- On the project's homepage, in the upper-right corner, select Fork ({fork}):

- Optional. Edit the Project name.
- For Project URL, select the namespace your fork should belong to.
- Add a Project slug. This value becomes part of the URL to your fork. It must be unique in the namespace.
- Optional. Add a Project description.
- Select the Visibility level for your fork. For more information about visibility levels, read Project and group visibility.
- Select Fork project.
GitLab creates your fork, and redirects you to the new fork's page.
Update your fork
To copy the latest changes from the upstream repository into your fork, update it from the command line. GitLab Premium and higher tiers can also configure forks as pull mirrors of the upstream repository.
From the command line
To update your fork from the command line, first ensure that you have configured
an upstream remote repository for your fork:
-
Clone your fork locally, if you have not already done so. For more information, see Clone a repository.
-
View the remotes configured for your fork:
git remote -v -
If your fork does not have a remote pointing to the original repository, use one of these examples to configure a remote called
upstream:# Use this line to set any repository as your upstream after editing <upstream_url> git remote add upstream <upstream_url> # Use this line to set the main GitLab repository as your upstream git remote add upstream https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab.gitAfter ensuring your local copy has the extra remote configured, you are ready to update your fork.
-
In your local copy, ensure you have checked out the default branch, replacing
mainwith the name of your default branch:git checkout mainIf Git identifies unstaged changes, commit or stash them before continuing.
-
Fetch the changes to the upstream repository:
git fetch upstream -
Pull the changes into your fork, replacing
mainwith the name of the branch you are updating:git pull upstream main -
Push the changes to your fork repository on the server (GitLab.com or self-managed):
git push origin main
With repository mirroring (PREMIUM)
A fork can be configured as a mirror of the upstream if all these conditions are met:
- Your subscription is Premium or higher.
- You create all changes in branches (not
main). - You do not work on merge requests for confidential issues,
which requires changes to
main.
Repository mirroring keeps your fork synced with the original repository.
This method updates your fork once per hour, with no manual git pull required.
For instructions, read Configure pull mirroring.
WARNING: With mirroring, before approving a merge request, you are asked to sync. You should automate it.
Merge changes back upstream
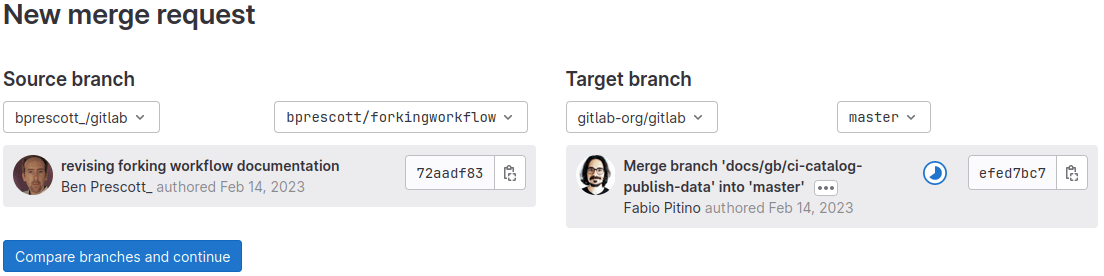
When you are ready to send your code back to the upstream project, create a merge request. For Source branch, choose your forked project's branch. For Target branch, choose the original project's branch.
NOTE: When creating a merge request, if the forked project's visibility is more restrictive than the parent project (for example the fork is private, the parent is public), the target branch defaults to the forked project's default branch. This prevents potentially exposing the private code of the forked project.
Then you can add labels, a milestone, and assign the merge request to someone who can review your changes. Then select Submit merge request to conclude the process. When successfully merged, your changes are added to the repository and branch you're merging into.
Unlink a fork
Removing a fork relationship unlinks your fork from its upstream project. Your fork then becomes an independent project.
Prerequisites:
- You must be a project owner to unlink a fork.
WARNING: If you remove a fork relationship, you can't send merge requests to the source. If anyone has forked your project, their fork also loses the relationship. To restore the fork relationship, use the API.
To remove a fork relationship:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Settings > General.
- Expand Advanced.
- In the Remove fork relationship section, select Remove fork relationship.
- To confirm, enter the project path and select Confirm.
When you unlink a fork that uses a hashed storage pool to share objects with another repository:
- All objects are copied from the pool into your fork.
- After the copy process completes, no further updates from the storage pool are propagated to your fork.
Related topics
- GitLab blog post: Keep your fork up to date with its origin
- GitLab community forum: Refreshing a fork
Troubleshooting
Error: An error occurred while forking the project. Please try again
This error can be due to a mismatch in shared runner settings between the forked project and the new namespace. See Forks in the Runner documentation for more information.
Removing fork relationship fails
If removing the fork through the UI or API is not working, you can attempt the fork relationship removal in a Rails console session:
p = Project.find_by_full_path('<project_path>')
u = User.find_by_username('<username>')
Projects::UnlinkForkService.new(p, u).execute