Operational Container Scanning (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 14.8.
- Deprecated the starboard directive in GitLab 15.4. The starboard directive is scheduled for removal in GitLab 16.0.
To view cluster vulnerabilities, you can view the vulnerability report. You can also configure your agent so the vulnerabilities are displayed with other agent information in GitLab.
Enable operational container scanning
You can use operational container scanning to scan container images in your cluster for security vulnerabilities. You can enable the scanner to run on a cadence as configured via the agent, or setup scan execution policies within a project that houses the agent.
NOTE: In GitLab 15.0 and later, you do not need to install Starboard operator in the Kubernetes cluster.
Enable via agent configuration
To enable scanning of all images within your Kubernetes cluster via the agent configuration, add a container_scanning configuration block to your agent
configuration with a cadence field containing a CRON expression for when the scans are run.
container_scanning:
cadence: '0 0 * * *' # Daily at 00:00 (Kubernetes cluster time)The cadence field is required. GitLab supports the following types of CRON syntax for the cadence field:
- A daily cadence of once per hour at a specified hour, for example:
0 18 * * * - A weekly cadence of once per week on a specified day and at a specified hour, for example:
0 13 * * 0
NOTE: Other elements of the CRON syntax may work in the cadence field if supported by the cron we are using in our implementation, however, GitLab does not officially test or support them.
NOTE: The CRON expression is evaluated in UTC using the system-time of the Kubernetes-agent pod.
By default, operational container scanning attempts to scan the workloads in all
namespaces for vulnerabilities. You can set the vulnerability_report block with the namespaces
field which can be used to restrict which namespaces are scanned. For example,
if you would like to scan only the default, kube-system namespaces, you can use this configuration:
container_scanning:
cadence: '0 0 * * *'
vulnerability_report:
namespaces:
- default
- kube-systemEnable via scan execution policies
To enable scanning of all images within your Kubernetes cluster via scan execution policies, we can use the scan execution policy editor To create a new schedule rule.
NOTE: The Kubernetes agent must be running in your cluster to scan running container images
Here is an example of a policy which enables operational container scanning within the cluster the Kubernetes agent is attached to:
- name: Enforce Container Scanning in cluster connected through my-gitlab-agent for default and kube-system namespaces
enabled: true
rules:
- type: schedule
cadence: '0 10 * * *'
agents:
<agent-name>:
namespaces:
- 'default'
- 'kube-system'
actions:
- scan: container_scanningThe keys for a schedule rule are:
-
cadence(required): a CRON expression for when the scans are run -
agents:<agent-name>(required): The name of the agent to use for scanning -
agents:<agent-name>:namespaces(optional): The Kubernetes namespaces to scan. If omitted, all namespaces are scanned
NOTE: Other elements of the CRON syntax may work in the cadence field if supported by the cron we are using in our implementation, however, GitLab does not officially test or support them.
NOTE: The CRON expression is evaluated in UTC using the system-time of the Kubernetes-agent pod.
You can view the complete schema within the scan execution policy documentation.
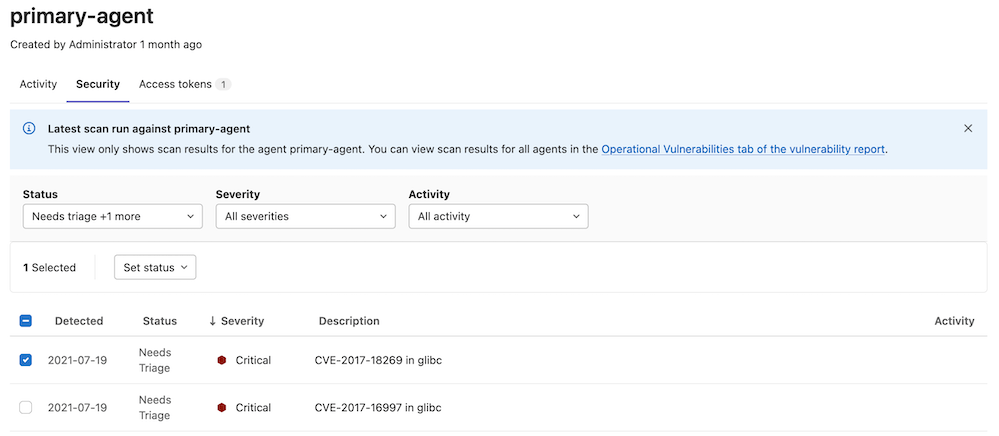
View cluster vulnerabilities
To view vulnerability information in GitLab:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find the project that contains the agent configuration file.
- On the left sidebar, select Infrastructure > Kubernetes clusters.
- Select the Agent tab.
- Select an agent to view the cluster vulnerabilities.
This information can also be found under operational vulnerabilities.
NOTE: You must have at least the Developer role.