- Introduction to the ncRNA Search Bar
- Tools in the ncRNA Search Bar
- Atlas Census
- Introduction
- Parameters for Adjusting Stringency for Detection
- Parameters for Adjusting Sample Subsets
- Downstream Analysis (for Mature miRNAs)
Introduction to the ncRNA Search Bar¶
The ncRNA search bar is designed to drill down on an ncRNA-specific level into the Atlas data.
For example, imagine I was very interested in the mature miRNAs hsa-miR-320a and hsa-miR-100-5p.
It would be nice if I could learn more about those mature miRNAs in the context of the Atlas.
Below, we'll learn exactly how to do that.
- Click the banner at the top of any page on the Atlas
- Click the Home button in the navigation bar at the top of any page on the Atlas
- Click Select Profiles in the navigation bar and then click ncRNA Search Bar
Below, you can see a picture of the ncRNA search bar (boxed in red):
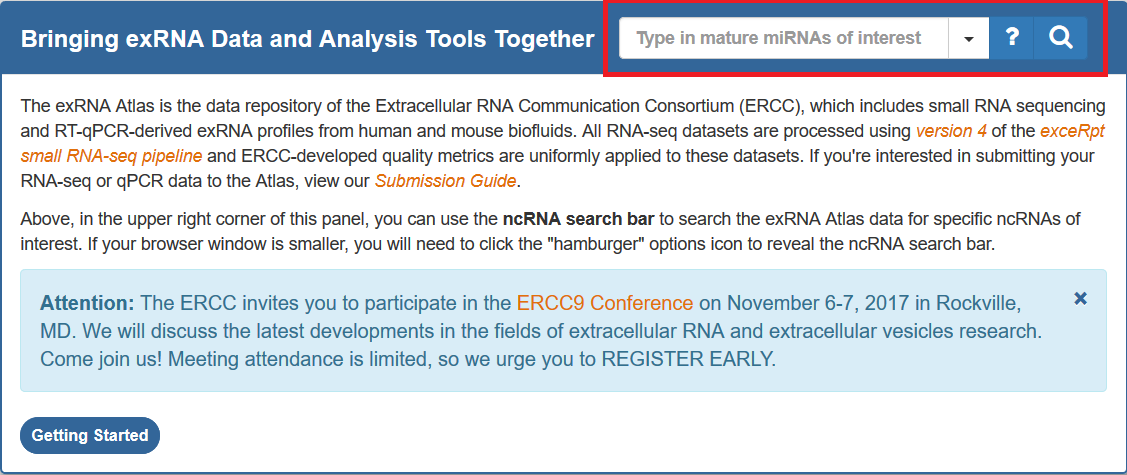
We recommend the following steps when learning how to use the search bar:
- Click the options icon directly to the right of the text box.
- You can select the type of ncRNA that you'd like to search for (mature miRNA, tRNA, piRNA).
- You can also select your desired database, but we currently only offer one (the Atlas Census, which will be explained further below).
- Once you've selected your type of ncRNA, you can type or paste your identifiers of interest into the text box.
- If you're not sure about how to format your identifiers, you can click the question mark button to bring up a help dialog.
- This help dialog will include example queries for each type of ncRNA, and you can even run an example query by clicking the "Run Example Query" button.
- Once you've written your identifiers of interest, you can click the magnifying glass (or hit enter) to perform your search.
- If you wrote any incorrectly formatted identifiers, an error page will be displayed with some helpful information.
- This error page will include the source database for the type of ncRNA, an example query, and other miscellaneous information.
- You will also see a list of correctly formatted identifiers and a list of incorrectly formatted identifiers.
- If you want, you can click the orange search text in the error panel to directly search for your correctly formatted identifiers (discarding the incorrect ones).
Below, we can see that I've typed three mature miRNA IDs into the search bar:

Two of these mature miRNA IDs are valid (hsa-let-7b-3p and hsa-miR-101-5p), while one is invalid (test).
When we click search, we'll see a page like this:

You can see that the page presents some useful information that will help us format our search correctly.
You can use this information to fix your incorrect identifiers, or, if preferred, just directly submit a search with your correct identifiers.
Tools in the ncRNA Search Bar¶
Once you've submitted a properly formatted request, a results page will be displayed.
We will break down the results pages for the different databases below.
Atlas Census¶
Introduction¶
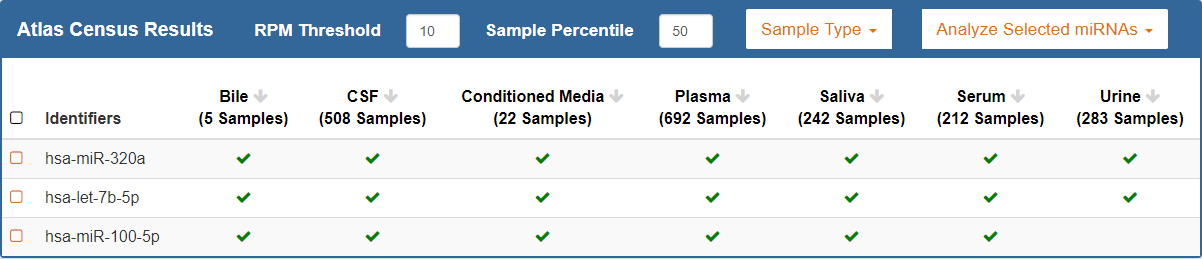
When you perform a search using the Atlas Census database, your results will consist of a table that summarize the frequency of your selected ncRNAs in the exRNA Atlas data.- Each row in the table will correspond to a selected ncRNA.
- Each column in the table will correspond to a biofluid found in the Atlas.
- The number of samples present for each biofluid will be displayed below the name of the biofluid.
- A checkmark in a given cell will indicate that the ncRNA was expressed in that biofluid according to the provided parameters.
- The absence of a checkmark does not mean that the ncRNA was not expressed in that biofluid.
- You can click a biofluid's column header to sort your results by that biofluid.
The parameters listed below will normally be displayed above the table. However, if your browser window isn't large enough to fit the parameters,
a hamburger menu will be made available in the upper right corner. Simply click the hamburger icon to reveal the different parameters.
Parameters for Adjusting Stringency for Detection¶
There are two parameters for adjusting stringency for detection of your ncRNAs:- RPM Threshold: For a given ncRNA in a given sample, what RPM (reads per million mapped reads) is required in order for that ncRNA to be considered expressed?
- Sample Percentile: For a given ncRNA in a given biofluid, the sample percentile controls the percentage of samples that must meet the RPM threshold in order for that ncRNA to be considered expressed in that biofluid.
Parameters for Adjusting Sample Subsets¶
You can also pick different subsets of the Atlas data for your table by using the Sample Type option.- For example, if you choose Healthy Samples, only healthy samples will be used when generating the table. More options will be coming soon.
- The number of samples below each biofluid will be updated accordingly after picking your new sample type.
Downstream Analysis (for Mature miRNAs)¶
Finally, if you searched for mature miRNAs (as opposed to tRNAs or piRNAs), you can perform downstream analysis on those mature miRNAs.
First, select your miRNAs of interest (via the checkboxes on the left side of the table).
You can then click the Analyze Selected miRNAs button above the table to see the different downstream analysis tools.
- Pathway Finder
- Use Pathway Finder (hosted by WikiPathways) to find pathways containing miRNAs of interest (or protein targets of those miRNAs).
- Click a given pathway title to visualize its contents at the bottom of the page.
- Then, select a given miRNA to highlight its associated target(s).
- The pathway visualization is interactive - zoom in or out by using the + and - icons, and click a given gene product to learn more about it.
- Designed and implemented by Kristina Hanspers, Anders Riutta, and Alexander Pico at the Gladstone Institutes, San Francisco, CA.
- Integrated into the exRNA Atlas by William Thistlethwaite and Neethu Shah at the Bioinformatics Research Lab, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX.